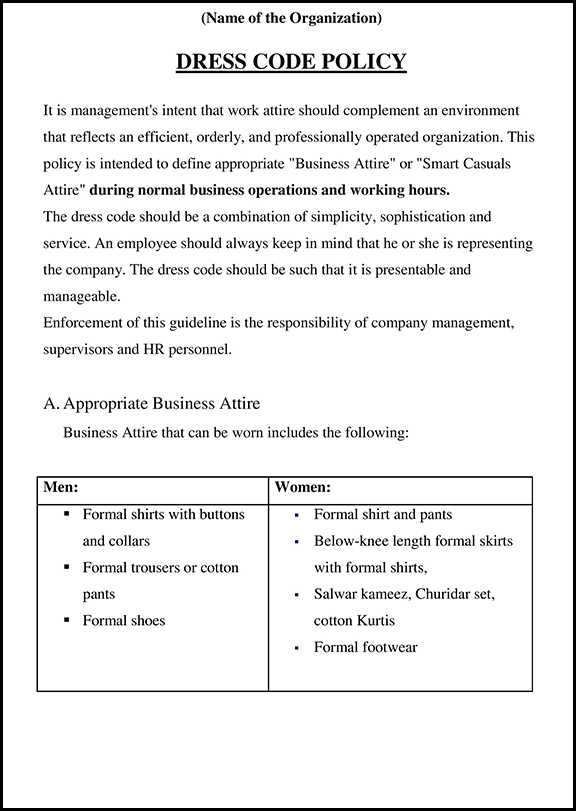
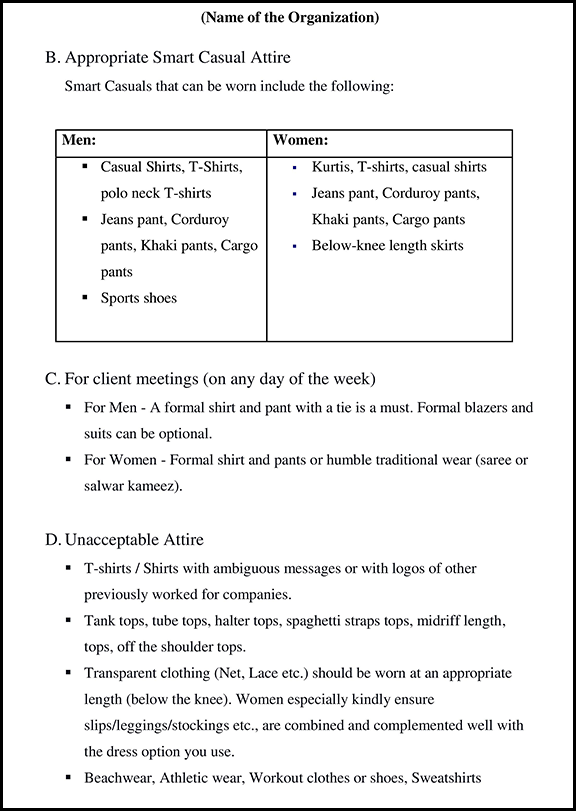
Maternity Leave in India 2025: Importance & Benefits
What is the Maternity Leave Policy?
Maternity leave is a crucial benefit for working women, ensuring their well-being during pregnancy and childbirth. The Maternity Benefit Act, introduced in 1961 and later amended in 2017, has played a pivotal role in protecting the rights of women employees in India. This policy provides paid leave, job security, and additional benefits for mothers, helping them balance their professional and maternal responsibilities.
The Maternity (Amendment) Bill 2017 brought a lot of necessary amendments in the Act. Let us understand:
Key Features of the Maternity Benefit Act 2017
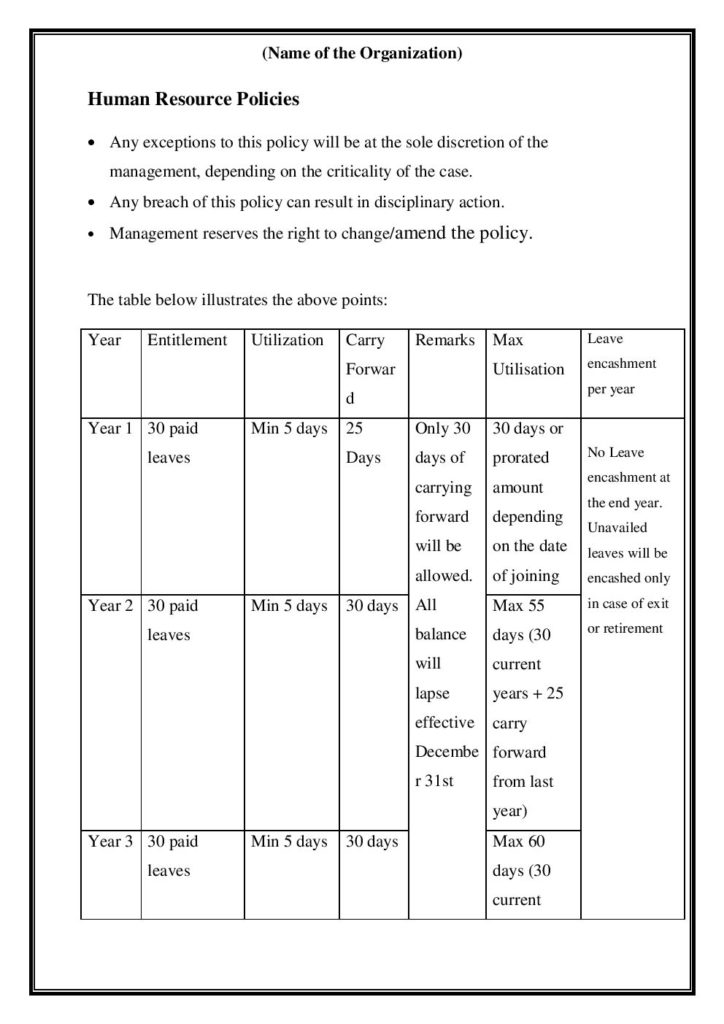
Extended Leave Duration: The maternity leave period was extended from 12 weeks to 26 weeks for the first two children. For subsequent children, the leave is 12 weeks. Additionally, 12 weeks of leave is granted to adoptive and commissioning mothers.
Flexibility: Women employees can take up to 8 weeks of maternity leave before the expected delivery date. The remainder of the leave can be taken post-delivery, up to a total of 26 weeks.
Job Security: The Act prohibits employers from terminating a woman’s employment during or due to maternity leave. Upon her return, she should be reinstated in her previous or equivalent position.
Payment During Leave: During the maternity leave period, women are entitled to full wages based on the average daily wage calculated over the three months prior to their leave.
Eligibility for Maternity Leave:
To qualify for maternity leave under the Maternity Benefit Act, the following criteria must be met:
Employment in Eligible Establishments: Women working in establishments with 10 or more employees are eligible for maternity leave benefits under the Act.
Work Duration: Women must have worked for at least 80 days in the 12 months preceding the expected delivery date to qualify for maternity leave.
Compensation and Benefits under the Maternity Leave Act 2017:
Medical Bonus: A medical bonus of Rs. 3500 is granted along with the maternity leave for eligible women employees.
Work-from-Home Option: Some organizations may allow remote work arrangements during or after maternity leave, depending on the nature of the work.
National Food Security Act Benefit: Pregnant women and lactating mothers are entitled to a benefit of Rs. 6000 under the National Food Security Act
Childcare Facilities: Organizations with 50 or more female employees are required to provide childcare facilities, ensuring that working mothers can conveniently care for their young children.
Norms Under The Maternity Leave:
1. The act states, the employer should not give a pregnant employee difficult tasks, including long-standing working hours, ten weeks before the delivery, such that it might affect both Mother and child.
2. The employer should ensure the health and safety of the female employer and mandate that she should not be involved in any work six weeks following the delivery as well as miscarriage.
3. The law also states that the employer cannot dismiss or discharge a female employer during the maternity leave period.
4. If an employer does not adhere to the Maternity Act, there are severe repercussions. The penalty to an employer for non-acceptance of the Act is a fine of Rs. 5000/- or imprisonment which can extend to a year or both.
Also Read: Top Startups in India 2024
Also Read: Sexual Harassment Policy
HR Considerations for Maternity Leave Act:
1. Every HR has to draft a detailed Maternity Leave Policy as an essential document. Every organization should communicate to a pregnant woman in writing or e-mail about her rights and the details thereof.
2. HR should revise the Maternity leave policy as per the government regulations.
3. A pregnant employee is by default, exempted from the regular performance appraisal cycle.
4. A provision to make the women employees work from home.
Alternate Policy for Maternity
There are different maternity acts under India offering maternity benefits. The Maternity Benefits Act stipulates that an organization cannot incorporate two different maternity acts at once.
ESI – Employees State Insurance
ESI is a self-financed plan and applicable for women employees, drawing a salary of 15,000/month or less. According to this Act, the employer contributes 3.25 % to the insurance, and the employee contributes 0.75 %.
The Factories Act 1948
The Factories Act ensures full wages for the 12 weeks of maternity leave.
FAQs on Maternity Leave Policy in India:
1. Is maternity leave paid?
Yes, it is paid according to the Indian Maternity Benefit Act 1961
2. Can maternity leave be extended under certain circumstances?
In certain circumstances, maternity leave can be extended beyond the specified duration, subject to approval from the employer and compliance with legal regulations
3. What documents are required to claim maternity leave?
To claim maternity leave, necessary documents such as medical certificates and application forms prescribed by the employer or government authorities may be required.
4. Are adoptive mothers entitled to maternity leave?
Yes, they are entitled to maternity leave in India, providing them with the opportunity to care for and bond with their newly adopted child.
5. Can an employer terminate an employee while on maternity leave?
Terminating an employee while on maternity leave is illegal under the Maternity Benefits Act, protecting women during this critical time.
Download : 1500+ Business & Legal Documents Templates
Join a Community of 1,00,000+ HR Professionals