IT Cyber Security Policy Template
IT Cyber Security Policy Template
Download Full Version
Created by India’s top HR experts
Just Rs. 999 Rs. 499
What is an IT Cyber Security Policy?
The IT Cyber Security Policy is a documented set of rules for protecting the company’s confidential data. Individuals with access to the company’s assets, login system, and technology are to adhere to the terms of the policy. This policy defines all the responsibilities and privileges of the users. In addition, you get a brief understanding of the internet access standards, acceptable use, user limitations, penalty for policy violations, etc. The document additionally comprises the protocols regarding how to promptly react to the specific incidents that threaten the overall security of the company’s data, network, and computer system.
What Should an IT Cyber Security Policy Include?
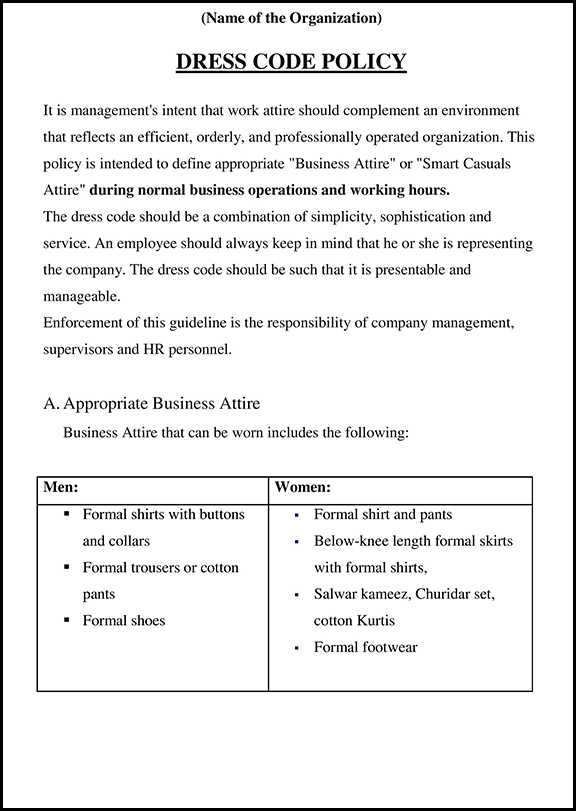
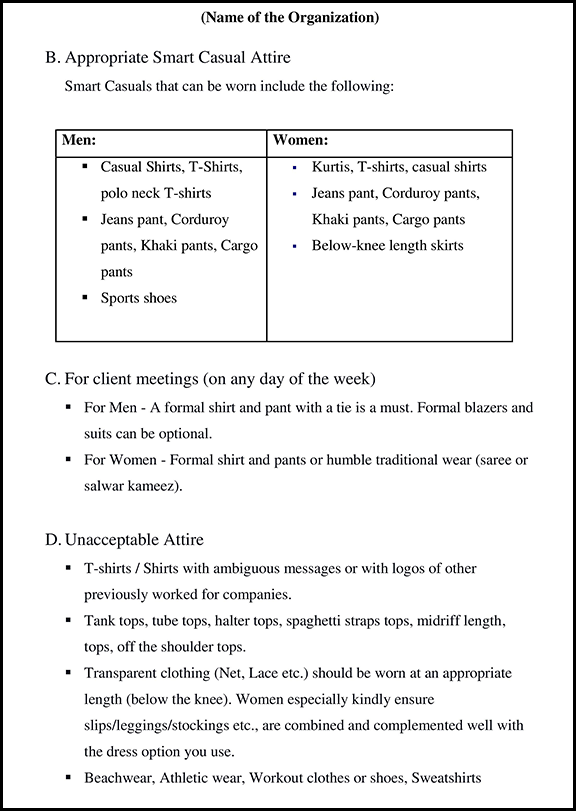
An IT Cyber Security Policy in India Includes the Following Things:
User Responsibilities
Users must understand and fulfill their responsibilities in order to maintain a secure digital environment within the organization. every member of the team, including employees, contractors, and authorized individuals, plays a crucial role in maintaining cyber security standards and mitigating potential risks. The following are the responsibilities that users must fulfill to ensure a secure digital environment.
1. Security Awareness:
Everyone must be up-to-date on cyber security threats and the best practices to prevent them. Regular training sessions and awareness programs are provided to ensure that all users understand the significance of identifying and responding to potential security risks, like phishing emails or suspicious website links.
2. Password Management
It is the responsibility of users to create robust and unique passwords for their accounts and systems. These passwords should not be shared with others, written down, or easily guessable. By following the organization’s password policy, users help maintain security measures.
3. Access Control
It’s important that users only access resources and data that are essential for their job duties. Any attempts to bypass access controls or escalate privileges without proper authorization can put the system’s security at risk, so it’s crucial for users to strictly follow established access control procedures.
4. Safe Internet and Email Usage:
It is crucial to exercise caution while browsing the internet and interacting with emails. Users should be vigilant in avoiding suspicious websites, refrain from clicking on links or attachments from unknown sources, and immediately report any suspicious emails or activities to the IT department.
5. Device Security:
Users have the responsibility to ensure the security of their devices, such as laptops and smartphones. This includes installing and regularly updating security software, enabling device encryption, and promptly reporting lost or stolen devices to the IT department to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
6. Compliance with Security Policies and Regulations:
It is the responsibility of users to adhere to all applicable security policies, procedures, and regulatory requirements that are applicable to their role and responsibilities, including industry standards and legal obligations related to privacy and data protection.
Confidential Data
1. Identification and Classification:
It is essential for users to accurately identify and classify confidential data according to its sensitivity and importance to the organization. This may include personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, intellectual property, or proprietary business information.
2. Encryption:
To ensure the security of confidential data, it is crucial to encrypt it when transmitting over networks or storing on portable devices like laptops, USB drives, or mobile devices. To safeguard data from unauthorized access or interception, users must employ encryption technologies.
3. Storage and Handling:
Users must store confidential data in secure locations, such as encrypted databases or password-protected folders. Physical documents with confidential information should be kept in locked cabinets or secure storage areas with access restricted to authorized personnel.
4. Transmission Security:
When transmitting confidential data electronically, it is crucial to use secure communication channels, such as encrypted email or secure file transfer protocols (SFTP), to prevent unauthorized interception or eavesdropping.
How To Use?
Fill In The Blanks
 Customize Template
Customize Template
 Save, Print, Done.
Save, Print, Done.
→ Editable in MS Word & Google Docs
→ Full Version
→ Created by India’s Top HR Experts
→ Used by HR professionals at Dream11, Razorpay, Tata 1mg, Mamaearth & 15k+
Rs. 999 Rs. 499
Download StartupHR Toolkit Instantly & Access Largest Collection HR Documents.
The only Toolkit to solve all your HR problems in minutes.
Legally compliant and govt approved HR documents.
24×7 customer support over chat & calls (during daytime).
FREE HR audit.
Up to date documents as per the latest Statutory Law.
3 FREE customized documents with Gold Plan.
Expert HR guidance.
Join a Community of 1,00,000+ HR Professionals