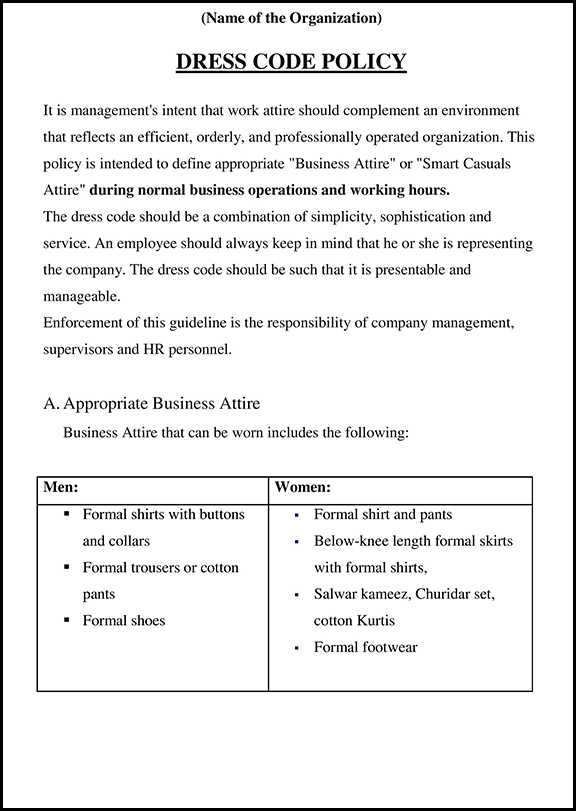
What is the Importance of a Non-Disclosure Agreement?
In today’s competitive business world, protecting confidential information is essential. Whether it’s your company’s trade secrets or customer data, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access is crucial for maintaining your competitive edge.
That’s the Importance of a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA).
An NDA is a legal document that establishes a confidential relationship between two parties.
It outlines the types of information that are considered confidential, the timeframe during which the information must be kept confidential, and the consequences for violating the agreement.
This blog will explore the What and Importance of a Non-Disclosure Agreement.
What is Non-Disclosure Agreement
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legal document that protects confidential information shared between two parties. It ensures that the information is confidential and cannot be shared with third parties without explicit consent. For businesses, an NDA is crucial as it protects their sensitive information, such as trade secrets, financial information, and client lists. It also ensures that employees, contractors, and individuals who have access to confidential information are legally bound to maintain its secrecy.
Overall, an NDA plays a vital role in safeguarding a business’s intellectual property and maintaining its competitive advantage.
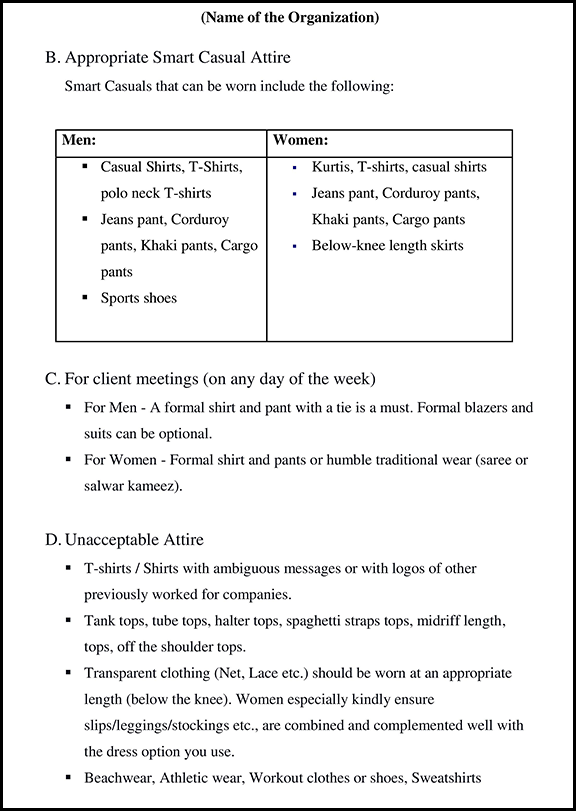
Key Elements of an NDA
1. Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) protect confidential information.
2. The agreement should clearly define what information is considered confidential.
3. NDAs should specify the purpose for which the confidential information can be used.
4. It is important to state the duration of the agreement clearly.
5. Outline the consequences of breaching the agreement
6. NDAs can be unilateral or mutual.
7. Confidentiality obligations survive termination of the agreement.
8. NDAs can be used to protect trade secrets, customer lists, and other sensitive information.
9. Legal counsel should review the agreement before signing.
10. NDAs protect a company’s competitive advantage and reputation.
Importance of a Non-Disclosure Agreement
1. Protect information
An NDA can help prevent the misuse of confidential information by unauthorized access. It sets out the terms of use and the consequences of breach. This clause can be particularly important when employees leave the company. An NDA can prevent them from using the information they gathered during their employment with your company for their benefit.
2. Intellectual Property
Intellectual property is one of the most valuable assets of any business. NDAs can protect your IP, including patents, trademarks, and copyrights, from being disclosed to competitors or others who may use it for their benefit. Without an NDA, your competitors could gain access to your trade secrets, which could lead to significant losses.
3. Protect Company Data
Businesses rely heavily on technology to carry out their operations. And with the increase in cyber threats, protecting company data has become more important than ever. One way to safeguard your intellectual property and confidential information is through a non-disclosure agreement (NDA). An NDA is a legal contract that forbids the recipient from sharing any confidential information obtained during the work with the company.
4. Company Goal and Objective
A company’s goals and objectives provide a clear direction and purpose for its operations. Goals are broad, long-term aspirations that guide the overall vision of the organization, while objectives are specific, measurable targets that contribute to achieving those goals. Goals define the desired outcomes, such as market leadership or revenue growth, while objectives outline the actionable steps and metrics to track progress.
5. International Business Considerations
When conducting business across borders, NDAs provide a standardized framework for protecting confidential information, regardless of the jurisdiction in which it is shared. They help establish clear expectations and legal obligations regarding the handling of sensitive data, trade secrets, proprietary technology, or other confidential information.
6. Business Plans and Strategy
A business plan outlines the goals, objectives, and strategies of the company, while a strategy is a set of well-defined strategic actions that are taken to achieve those goals. Without an NDA, sensitive information can be leaked, leading to a loss of competitive advantage and potential revenue.
7. Marketing and Sales Information
NDAs ensure that sensitive marketing strategies, customer data, pricing structures, and other proprietary information remain confidential. By requiring employees, contractors, and external partners to sign NDAs, businesses can prevent the unauthorized disclosure of valuable marketing and sales information to competitors or unauthorized parties.
When do You need NDA?
1. Partners
When forming partnerships or joint ventures, NDAs are crucial to establishing confidentiality obligations between the involved parties. This ensures that sensitive information, such as trade secrets, financial data, or proprietary technology, remains protected within the partnership.
2. Investors
Startups or businesses seeking investments require potential investors to sign NDAs. This safeguards confidential financial projections, business plans, or proprietary technology shared during the investment process, assuring the investors that their information will be kept confidential.
3. Employees
NDAs are commonly used with employees to protect trade secrets, client information, and other proprietary details to which they have access during working in the company. This ensures that employees understand their obligations to maintain confidentiality even after leaving the company.
4. Freelancers
When hiring freelancers or independent contractors, businesses may require NDAs to protect confidential information shared during the engagement. This prevents freelancers from disclosing or misusing the information for their own gain or sharing it with unauthorized parties.
5. Suppliers and Vendors
NDAs are important when sharing sensitive information with suppliers or vendors, such as pricing structures, manufacturing processes, or proprietary specifications. This safeguards the shared information and ensures that suppliers and vendors maintain confidentiality to protect the business’s interests.
How NDAs Work
1. Create an Agreement
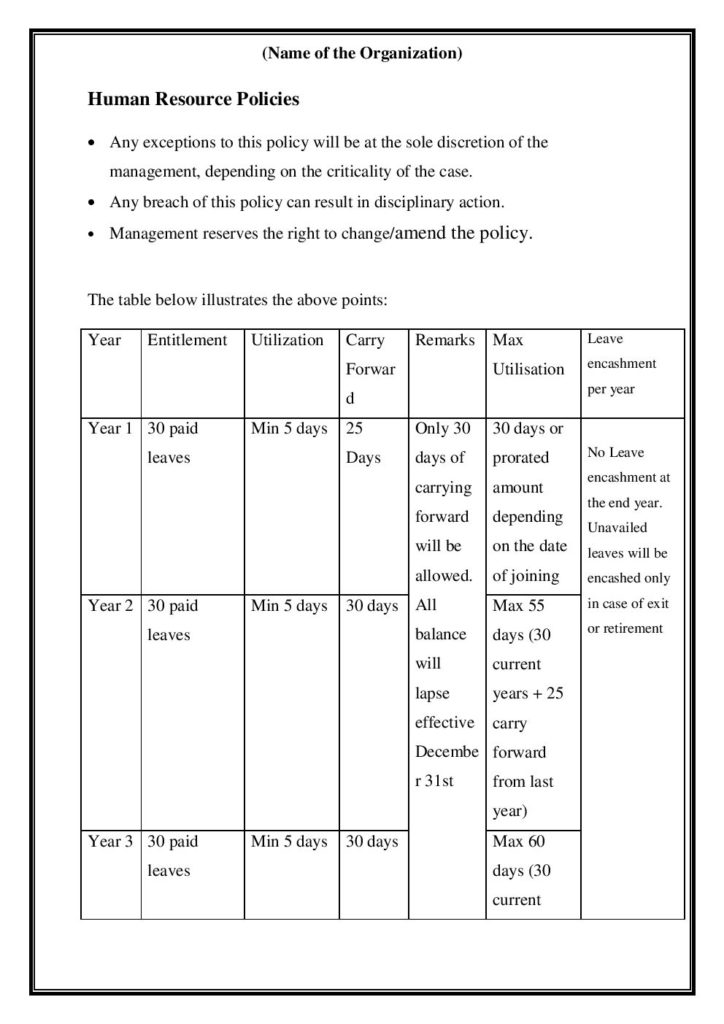
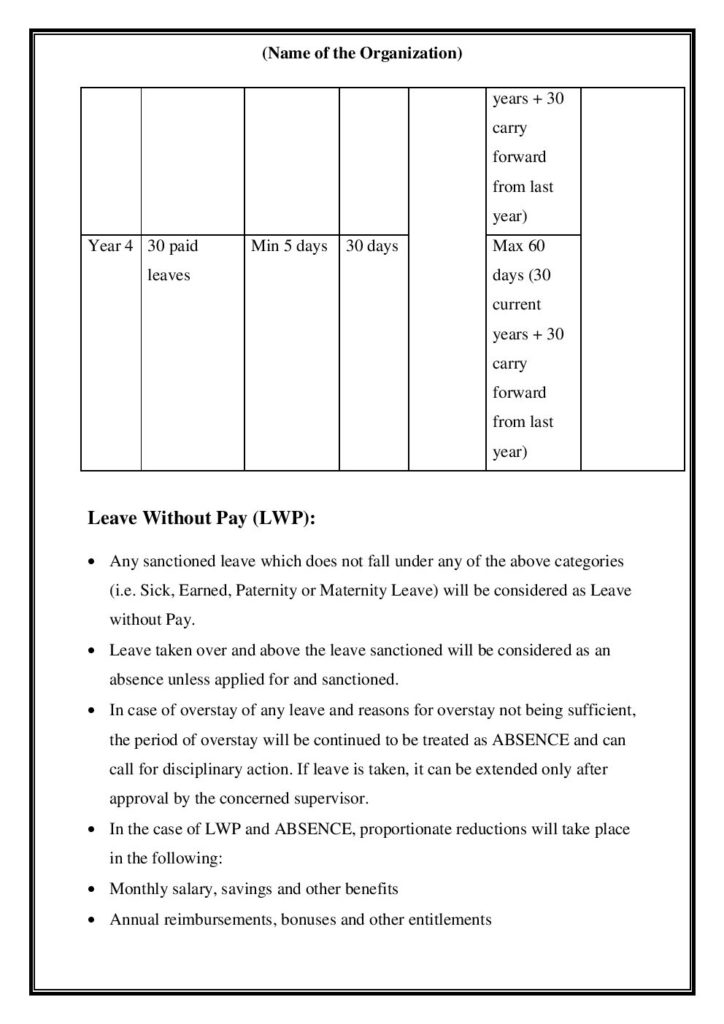
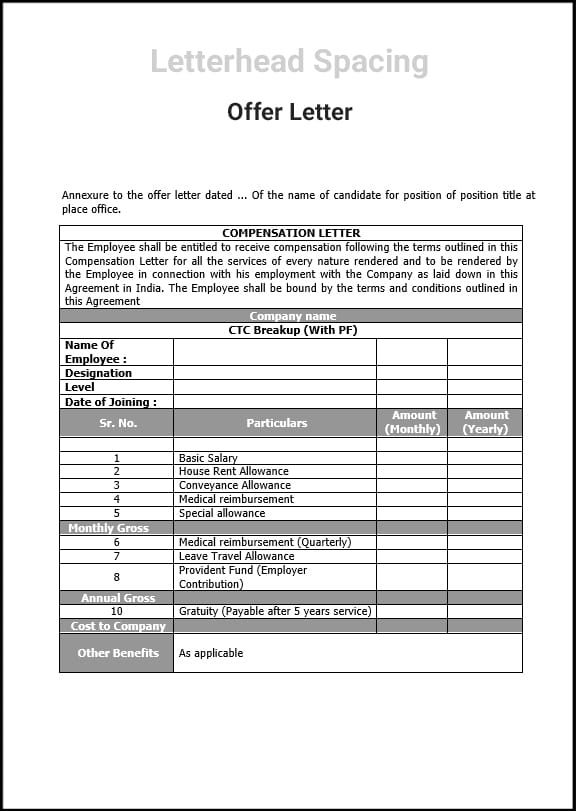
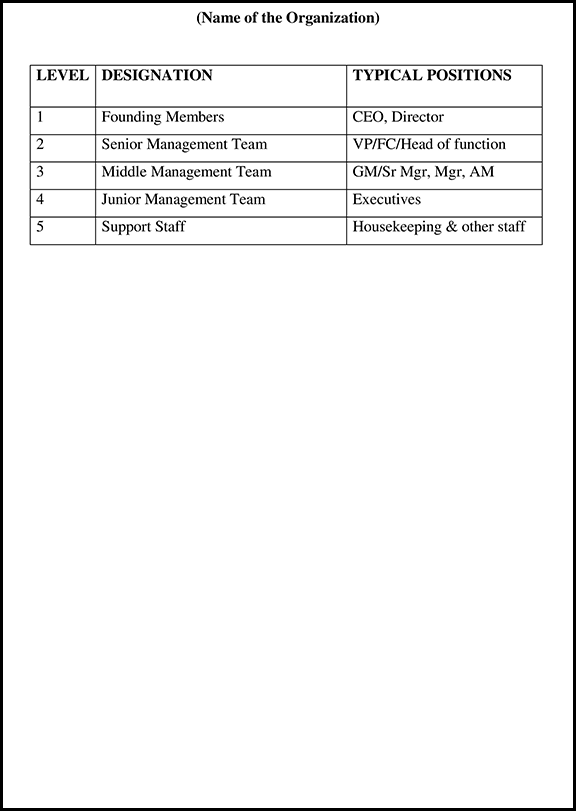
StartupHR Toolkit is a comprehensive resource that offers various tools and templates to assist startups and businesses in their human resources processes. When it comes to Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), the StartupHR Toolkit provides a template that can be customized in Word, pdf format.
The template typically includes standard sections such as definitions of confidential information, obligations of the recipient party, exclusions from confidentiality, duration of the agreement, and consequences of breach.
2. Obligations of the Receiving Party
The NDA outlines the rights and responsibilities of the recipient regarding confidential information. This includes obligations such as maintaining confidentiality, not disclosing the information to unauthorized parties, and using the information solely for the intended purpose.
3. Exclusions from Confidentiality
Certain exceptions may apply, excluding specific information from the scope of confidentiality. These exclusions typically include data that is already publicly available or known to the recipient prior to signing the Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA). Additionally, information obtained independently by the recipient or lawfully disclosed by a third party may be excluded. These exclusions ensure that the NDA does not restrict the recipient’s use of information already in the public domain or obtained through lawful means, allowing for a balanced approach to confidentiality while respecting existing knowledge and sources.
4. Time Period of Agreement
The time period of the agreement can vary depending on the specific needs and circumstances, typically ranging from months to years. It is important to clearly define the duration within the Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) to specify when the obligations of confidentiality begin and end. This makes sure that both parties are aware of the timeframe during which the confidential information should be protected, promoting clarity and effective management of confidential information.
5. Remedies
Finally, the NDA should specify the remedies that will be available if the receiving party breaches the agreement. This can include injunctive relief, monetary damages, or both. The remedies should be sufficient to compensate the disclosing party for any harm that is caused by the breach.
Non-Disclosure Agreement Sample
1. Introduction
- Title: Clearly state that the document is a Non-Disclosure Agreement.
- Parties: Identify the parties involved, including the disclosing party (Discloser) and the receiving party (Recipient).
2. Definitions
- Confidential Information: Clearly define what includes confidential information, providing examples and specifying what is included and excluded from the agreement.
- Purpose: Describe the purpose for which the confidential information will be shared.
3. Confidentiality Obligations
- Non-Disclosure: Specify the Recipient’s obligation to maintain the confidentiality of the disclosed information.
- Non-Use: State that the recipient shall not use the information for any intention other than the specified purpose.
- Protection Measures: Outline the steps the recipient must take to safeguard confidential information from unauthorized disclosure.
4. Permitted Disclosures
- Exceptions: Identify specific situations where the recipient may be permitted to disclose the confidential information without breaching the agreement, such as when required by law or with prior written consent from the Discloser.
5. Term and Termination
- Duration: Specify the period during which the NDA will remain in effect. It can be a fixed duration or continue indefinitely.
- Termination: Outline the conditions under which either party can terminate the agreement, including provisions for early termination or expiration.
6. Remedies and Injunctive Relief
- Breach of Agreement: Describe the consequences of a breach, including the legal remedies available to the Discloser, such as monetary damages or injunctive relief.
- Governing Law: Specify the jurisdiction and laws that will govern the implementation and jurisdiction of the agreement.
7. Miscellaneous
- Entire Agreement: Clarify that the NDA constitutes the complete agreement between the parties and replaces any prior oral or written agreements.
- Severability: State that if any provision of the NDA is found to be invalid or unenforceable, the remaining provisions will still be effective.
In conclusion, the importance of a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) cannot be overstated. It serves as a crucial tool for businesses to protect their confidential information and maintain a competitive edge. With resources like the StartupHR Toolkit, businesses can conveniently create tailored NDAs that establish clear obligations and safeguards for confidentiality.
By utilizing such tools, businesses can mitigate risks, foster trust in their relationships, and confidently share sensitive information, knowing that the necessary legal framework is in place. Safeguarding valuable assets through NDAs is an essential practice for any organization that values the importance of a Non-Disclosure Agreement in safeguarding its sensitive information.
Join a Community of 1,00,000+ HR Professionals